Configuring External Authentication using Microsoft Active Directory / LDAP¶
Overview¶
TeamDrive support external authentication using a Microsoft Active Directory or LDAP compatible server. In this chapter we discuss how to setup the LDAP compatible external authentication available from TeamDrive.
See External Authentication for a general discussion of external authentication in TeamDrive. How to install an External Authentication Service is also described in External Authentication.
The communication between the authentication service and the directory service (LDAP or AD) is performed without encryption by default. If these services communicate via an untrusted network, we strongly advise to enable some form of encryption, to protect against the potential eavesdropping of usernames and passwords. For example, LDAP supports encryption via SSL (LDAPS), other alternatives would be using a VPN or an SSH tunnel.
Active Directory¶
This section covers the Authentication of a TeamDrive Client using the Active Directory directory service offered by Microsoft Windows Servers. Since Windows Server 2008, this is also referred to as ADDS. ADDS manages various objects on a network such as users, groups, computers, services, servers, and shared folders. With the help of Active Directory, an administrator can organize, deploy, and monitor the information of these objects.
Configuring Microsoft Active Directory Server¶
Managing Users¶
In the Server Manager, in the “Active Directory User and Computer” branch, create a new Organizational Unit with a meaningful name (“TeamDrive” for example). Select this newly created Organizational Unit and right click the middle panel to create a new user.
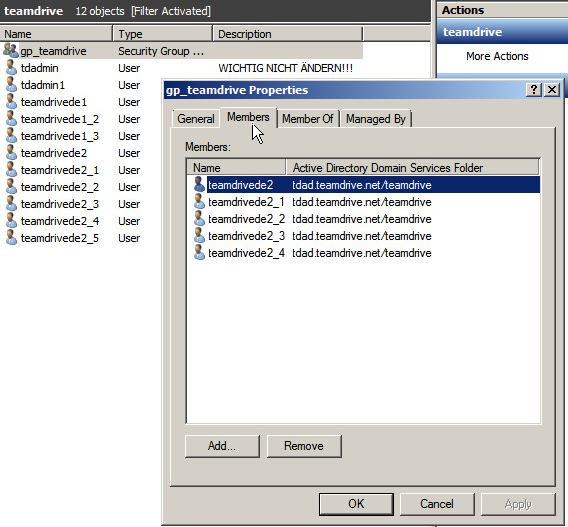
All users require an email address and need to be part of the group “gp_teamdrive”.
In this picture it can be seen that the user is a member of the group “gp_teamdrive”.
The following example assumes Red Hat Enterprise Linux 9 or a derivative like
CentOS Stream 9. The names of packages or with dnf: httpd, php,
php-pear, php-ldap, php-mcrypt.
LDAP/AD Service Configuration¶
Once you have installed the external Authentication Service code, you
must duplicate the file ldap_config.php.example, and rename it to
ldap_config.php (add this file to fapoilcy as described in
fapolicyd). The settings in this file must then be edited to
access your LDAP or AD service.
In general, optional parameters may be set to “”.
You must set the following configuration parameters: $service_name,
$reg_server_name, $provider_code and $allowed_origins. Configuration
parameters that are common to all External Authentication Service are described
here: Standard Configuration Parameters.
If you set $enable_debug = true during testing of the LDAP connection then
a trace of the LDAP/AD login attempt will be printed to the HTML page. In
production this variable must be set to false.
For querying LDAP/AD, this implementation uses the LDAP functionality of the PEAR “Auth” module. Since this module is no longer externally maintained, an updated version (compatible with PHP 8.3) is included directly in the TeamDrive distribution. More information can be found at the URL http://pear.php.net/package/Auth/docs.
The configuration file contains parameters which the set the PEAR Authentication fields. The examples use values for an Active Directory query.
Connection Parameters¶
These parameters are required.
$ldap_server_domain:This is domain name of the host on which the LDAP server is running.
$ldap_server_port:This is the port on which the LDAP server is listening. The default port for LDAP is 389.
Note
Please check if the LDAP server can be reached from the Apache Web Server. The access might be blocked if SELinux is enabled. You can check this:
[root@authserver ~]# getsebool -a | grep http | grep ldap
If you get ``httpd_can_connect_ldap --> off`` you have to allow the
communication or disable SELinux as described in :ref:`disable-selinux`.
$ldap_basedn:This is the base “distinguished name” of the part of the Directory that will be searched. Examples: “dc=teamdrive,dc=com”, “dc=egco,dc=teamdrive,dc=net”
Authentication¶
If the LDAP server does not allow anonymous connections then you must provide credentials for the connection here.
$ldap_binddn:This is the name of the user that has access to the part of the directory that is to be searched. For example: “cn=Manager,dc=teamdrive,dc=com”, “cn=TDAdmin,ou=global,ou=kkh,egco=tdad,dc=teamdrive,dc=net”,
$ldap_bindpw:The password of the user.
User Attributes¶
A number of user attributes can be sent to the TeamDrive Client after successful authentication. The user_id and email are required.
$ldap_user_id_attr:This is the name of the attribute which contains a unique identifier of the user. Usually this value is “uid”.
In order for external authentication to work the LDAP/AD server must store a unique, unchanging, identifier for each user. Note that if the identifier changes TeamDrive will fail to recognise The user, and assume the user is new. For this reason the email address is not a choice.
$ldap_email_attr:The name of the attribute that contains the user’s email address. Note that this email address is used within TeamDrive in order to invite users to a Space.
$ldap_common_name_attr:This is the name of the attribute that contains the user’s common name. If provided, TeamDrive will display this name, instead of the email address in the user interface.
$ldap_telephone_attr:This attribute contains the user’s home or work telephone number.
$ldap_mobile_attr:This attribute contains the user’s mobile telephone number.
User Identification¶
These parameters are required. They are used to locate a user in the directory.
$ldap_userdn:This specifies the user distinguished name to be searched.
$ldap_userdnis added to$ldap_basednwhen performing the search.$ldap_userattr:This parameter specifies the attribute that will be searched for the user’s “login name”. Any parameter that uniquely identifies the user may be used.
$ldap_userfilter:This is added to the search filter when searching. It is usually used to specify the object type of the users, for example: “(objectClass=inetOrgPerson)” or “(objectClass=posixAccount)”
Group Specification¶
By specifying a group you can ensure that only users of a particular group are authorised to access TeamDrive.
Use the parameters below to to determine how to check whether a user is a member of a group.
$ldap_groupdn:If this variable is empty, then no group check will be performed. The value of
$ldap_groupdnis added to$ldap_basednwhen searching for a group.$ldap_groupscope:The scope for group search, either
one,sub, orbase.subis the default.$ldap_groupfilter:This is added to the search filter when searching for a group. It usually identifies the group object type, for example: “(objectClass=groupOfUniqueNames)”.
$ldap_group:This is the name of the group to be searched. User’s that wish to Login to TeamDrive must be members of this group.
$ldap_groupattr:This variable specifies the group attribute to searched forto find the group name:
$ldap_group.$ldap_memberattr:This is the attribute in the group object that specifies the names of the members.
$ldap_memberisdn:Set this variable to
trueif the$ldap_memberattris the complete distinguished name (dn) of the user. If not, it is assumed to be just the value of the the memberattr is the dn of the user (default) or the value$ldap_userattrattribute.
Authentication Procedure¶
The ldap_login.php page generates an HTML form
with standard fields to collect the user’s credentials and generate the required
query with it. If the authentication was successful, the PHP code of the login
page generates the authentication token based on information returned from the
directory server (Active Directory) and returns it to the client.
The HTML form also includes some hidden fields, which are evaluated by the TeamDrive Client. In these fields the Registration Server’s name and the Provider Code are included.
The values are taken from the $reg_server_name and $provider_code settings.
<div id="loginFormWrapper">
<form id="loginForm" action="ldap_login.php" method="post" enctype="multipart/form-data">
<input type="hidden" id="td_login_page" value="login" />
<input type="hidden" id="td_registration_server" value="TeamDriveMaster" />
<input type="hidden" id="td_distributor_code" value="EGCO" />
Note
The content of the authentication token that is returned to the client is
encrypted with a secret key. This key is stored in the $token_encryption_key
parameter.
For debugging the generated query for the Active Directory, it is helpful to
have the debugging information display in the browser, by setting $enable_debug
to true.
Output is written to the login page, for example:
After the Authentication Service has confirmed the credentials of a user, an authentication token is passed to the TeamDrive client. The client then sends the token on to the registration server to complete the registration. Before the login process can be successfully completed, the registration server then verifies the authentication token by sending it to the Authentication Service.
Note
If you use SSL to encrypt the token verification communication between the
Registration Server and the Authentication Service (by providing an URL
starting with https:// in the VERIFY_AUTH_TOKEN_URL), you must
install properly signed SSL certificates on the Auth Service’s web server
— using self-signed certificates will result in an authentication
failure, displaying the error message REG SERVER EXCEPTION "-24918" ( "0"
) "Verify authentication failed: result file not found" in the Client log
file. You can use the command line tool curl on the Registration Server
to test opening the verification page. It should not complain about SSL
certificate problem: self signed certificate or other SSL-related problems
when opening the URL. Check your SSL configuration using the service from
SSL Labs: https://www.ssllabs.com/ssltest/analyze.html and make sure that
the “Handshake Simulation” is working for current platforms and browser. The
following ssl parameters for the apache web server will create an A-rating
and make sure that the handshake is working for current platforms and browser:
SSLProtocol all -SSLv2 -SSLv3
SSLHonorCipherOrder on
SSLCipherSuite ECDH+AESGCM:DH+AESGCM:ECDH+AES256:DH+AES256:ECDH+AES128:DH+AES:ECDH+3DES:DH+3DES:RSA+AESGCM:RSA+AES:RSA+3DES:!aNULL:!MD5:!DSS
To complete the registration process, the registration server requires the user’s ID and e-mail address. If the validation is successful, this information is sent back from the site as confirmation.
Server Configuration¶
As described in Services, all external authentication services must be registered.
To use the service once it is registered you must either setup a domain that references the authentication service or you must setup the authentication service as the default for a Provider.
To do this, set AUTH_SERVER_NAME to the name of the authentication service.