External Authentication¶
TeamDrive supports external authentication. If used, the authentication data is not located on the Registration Server. External authentication is performed by a Web-site called an “External Authentication Service” TeamDrive provides a number of standard implementations for Authentication Services, including: Azure, Google, LDAP, Microsoft Activate Directory, Vasco IDENTIKEY Authentication and standard Oauth 2.0 authentication. These will be referred to collectively as “Authentication Providers”.
Services such as LDAP and AD access company resources and therefore must be deployed within the corporate network. This associated Registration Server, on the other hand, may be located anywhere on the internet. Security is ensured by exposing only 2 access points: the login and verify URLs (see the description of Login URL and Verify URL below).
The HTML pages exposed by the External Authentication Service can be customised with the to reflect the CI (Corporate Identity) of the owner of the service.
All external authentication services must be registered on the Registration Server, see: Services.
To support external authentication, the mobile TeamDrive App (and older desktop Clients) provide access the External Authentication Service using an embedded browser. In this case the login is displayed in an alternative panel of the login dialog, following the entry of the user’s email address.
The latest TeamDrive Desktop Clients launch a local browser to access the External Authentication Service. This method uses “session-based” authentication. The Desktop Agent UI or the Web Portal redirect to the External Authentication Service as necessary.
In the first step of the login process the user must enter their email address. If the user is not already know to the Registration Server, the domain of the email address is used to determine the associated External Authentication Service. Login with an email address, rather than a “username”, is therefore required for login using an External Authentication Service.
Contact TeamDrive support in order to receive assistance in setting up your own an External Authentication Service.
If you are running external authentication services setup prior to version 4.5.1 (12 April 2020) of the Registration Server, then “unnamed” services must be upgraded to a named authentication service. See Upgrading External Authentication Services below for details.
Authentication Service Implementations¶
If you need to use an Authentication Service, TeamDrive provides a number of implementations as mentioned above.
If an implementation is not available for your authentication service, then it is possible to create a custom implementation using the “example implementation” as a template (see below).
Authentication Service Installation¶
An authentication service can be deployed on most Linux systems that supports Apache and PHP 8.3 or later. All TeamDrive implementations have been tested on CentOS 9 and therefore this is the recommended system.
The host providing the authentication service needs to be reachable by the TeamDrive Clients via HTTPS (TCP Port 443) as well as by your Registration Server via HTTP (TCP Port 80), if both systems are in a trusted environment, otherwise HTTPS (TCP Port 443).
Install the External Authentication Service package as described in
Installing the Registration Server External Authentication (optional). This package is also installed on the TeamDrive
Registration Server Virtual Appliance (in directory /var/www/html/authservice),
however, for security reasons, an authentication service should run
on the same host as the Registration Server.
On a minimal system, make sure that the following packages have been installed
with yum: httpd, php, php-ldap, php-mcrypt and
openldap-clients.
Configuration and Setup¶
After installation duplicate the *_config.php.example file of the service you
wish to use, and rename it to *_config.php.
You must set the following configuration parameters: $service_name,
$reg_server_name, $provider_code and $allowed_origins which are common
to all authentication service (see below for details of these settings).
Below these settings you will find a section of settings that are specific
to the type of service, LDAP, OAUTH2, etc. Set these parameters as required
by your service. Detailed comments in the config file describe what is
required for each parameter. For AD/LDAP setup, see :ref:ldap_parameters
for further details.
When the service name has been determined, and other settings such as Registration Server and Provider, you must register the External Authentication Service on the Registration Server. This must be done before you can test the service because, when called for the first time, the authentication service will attempt to verify the existence of the service on TDNS (the TeamDrive Name Server).
To register an authentication service you must enter 2 URLs: the Login URL
and the Verify URL. The Login URL must reference the *_login.php page
of your service, and the Verify URL must reference the *_verify.php page
of your service. See Services for more details on how to registered an
authentication service.
The Login URL is the start page for user’s using the authentication service. For testing purposes you can call this page directly from the browser. During TeamDrive login the TeamDrive Client will redirect to this page to begin the authentication process. Depending on the External Authentication Service, this page will then either display a login dialog, or redirect to the login page of the Authentication Provider (Google, Azure, etc.).
On successful login, Login URL page issues an “Authentication Token” which
can be verified by the Registration Server using the Verify URL. For testing
purposes, set $enable_debug = true in the configuration file, and you will
then be able to check the verification page, ater login. But, remember to
remove this debug before you system goes live.
Standard Configuration Parameters¶
There are a number of configuration parameters that are common to all authentication services:
$service_name: This must be set the unique name of the External Authentication Service a described in Services.$reg_server_name: Set this parameter to the name of your Registration Server.$provider_code: This is the Provider code of the Provider associated with this External Authentication Service.$allowed_origins: This setting is a list of URLs, that are the permitted origins (or “referrers”) for calls to the External Authentication Service.The TeamDrive Agent UI or Web Portal, when calling an External Authentication Service must specify a “referer” URL, which is checked against this list. If it is not in the list, an error will occur. After login, the browser is redirected back to the referer page.
Note that if a referrer URL is not provide, but is required, then the first URL in the
$allowed_originslist will used, and after login the browser will be redirected back to this URL.$webportal_domain: This setting is deprecated, and is no longer used. When upgrading to the latest version of the LDAP authentication service, copy the value of this variable to the position of the first URL in$allowed_origins(see above) array.$user_secret_salt: This random sequence of characters must be unique for each installation. Once set, this value may never change. It is also important that this value remains secret at all times as it is used to generate the, so-called, “User Secret” value, which is used to encrypt the user’s Key Repository stored on the Registration Server.On installation, leave this value blank, as found in the
*_config.php.examplefile. The value will then be automatically set to a 54 character random sequence when first used. On upgrade, ensure that the value from the previous version is preserved.Changing the value will result in users not being able to access their Key Repositories, which means that the user will not have access to their Spaces after a new TeamDrive installation.
However, access can be restored for the new device if the user has an old device and “Force Re-login” is requested from the Registration Server Admin Console.
$prev_user_secret_ver: This variable need only be set when upgrading from a previous version of the External Authentication Service, that used an older method to generate the User Secret (see above).Note
If you are upgrading from a version prior to version 4.5.1 (12 April 2020) then this variable must be set appropriately in order to ensure migration does not disrupt user access to the Registration Server Key Repository.
See Upgrading External Authentication Services for further details on how to set
$prev_user_secret_ver.$token_encryption_key: This random sequence of characters is used as a key to encrypt the authentication token sent to the client. The value must be unique for every installation.On installation, leave this value blank, as found in the
*_config.php.examplefile. The value will then be automatically set to a 54 character random sequence when first used.This string may be changed at any time since authentication tokens are only valid of a short time.
$enable_debug: Places links in the login page which allow you to retry login and provide a link to test the authentication token generated.
Authentication Service Customisation¶
You may change the user interface of the authentication services provided by TeamDrive by modifying the layout and content of the following files:
/authservice/*/index.html: This is the default page, which redirects to*_login.phpby default./authservice/*/*_login.php: You can change this page to present a login page that would be recognised by your users. For example, change the page to conform to you companies CI (Corporate Identity).
Note that all changes you make to other files under the authservice
directory will be overwritten when you update to the latest
td-regserver-ext-auth RPM. As a result, make sure that you make a backup
of these files before performing an upgrade.
Before making any changes to these files, make a backup copy of the file. You can them use this copy to determine if changes have been made to the file in subsequence versions of the External Authentication Service. These changes can then be incorporated in you version of the files.
Example Template Authentication¶
The “example authentication service” implementation provided can be used as a template to create your own External Authentication Service.
The example implementation stores the login names and email address of user in a text file. A page, “eg_register.php” may be used to create example users for testing the implementation.
Before beginning your customisation, make a copy of the “eg” directory, and
replace the prefix for all files, for example, change “eg_* to “myco_*” to
create an Authentication Services for “My Company”. Internal reference to pages
like <form action="eg_login.php" method="post" enctype="multipart/form-data">
must also be changed accordingly.
The functions in “eg_functions.php” must be customised for your system. For example, replace the implementation of getUserByLoginName() with code that retrieves users of your authentication system.
The file “eg_config.php”, contains the configuration parameters that are required by all External Authentication Services. This file is created by duplicating the “eg_config.php.example” file and renaming it to “eg_config.php”.
Configuration parameters include $service_name which must be set to the name
of the service. The other parameters are documented in detail in the file
“eg_config.php.example” file.
Add your service specific parameters to your own “myco_config.php.example” file, and set them as required in your services “myco_config.php” file. You should do this by replacing the “EXAMPLE PARAMETERS” section in the config file.
External User Registration¶
Note that a user that can successfully login to an External Authentication Service does not have to be “pre-registered” on a TeamDrive Registration Server. After successful login, if the user is unknown to TeamDrive, a user account is automatically created for the user. After this point the user is visible in the Registration Server Admin Console.
External authenticated users can, if required, be pre-registered in the Admin Console. In this case, the Registration Server will use the email address to identify the user, and set the external authentication ID (Ext Auth ID) of the user (see below).
Once the user has been assigned an Ext Auth ID the connection between the TeamDrive user and the externally authenticated user has been established and can no longer be changed.
External User Data¶
In order to support externally authenticated users, the Registration Server requires an external authentication ID (“Ext Auth ID”) and the email address of the user.
Ext Auth ID¶
A vital prerequisite for the external authentication is a unique fixed external authentication ID (in short: Ext Auth ID). The Authentication Service must provide a unique ID for every user that can be authenticated by the service. Furthermore, the Ext Auth ID must remain fixed from the the moment it is first used to identify a user.
The Ext Auth ID may be any character sequence up to 100 characters in length. The character sequence used as the Ext Auth ID is an internal reference which will not be exposed to the user. This means the character sequence can be cryptic (i.e. it does not need to make sense to the user). The most important characteristics of the Ext Auth ID is that it’s unique and unchanging.
Most systems to do not have a problem providing a unique identifier for a user. Note that,in general the email address of the user should not be used as the Ext Auth ID, even if it fixed. Generally authentication system have a global unique user identifier which is appropriate for an Ext Auth ID.
Note that if this identifier changes at some point the associated TeamDrive user will incur a disruption of the TeamDrive service, including failure to login and loss of access to Space Keys stored in Registration Server Key Repository.
Email Address¶
Users that have been externally authenticated will be identified in the TeamDrive Client by their email address. Invitations sent to externally authenticated users must also use the user’s email address.
The user’s email address may be changed in TeamDrive or in the external system. If the change is made externally to TeamDrive then the Registration Server will only discover the change when the user logs in again. This will not happen automatically, but it is possible to force user re-login using the Registration Server Admin Console, see Compelling Re-login below.
Compelling Re-login¶
You may need to compel the user to re-login for a number of reasons:
- Updating user information (email address and other profile information) stored by the TeamDrive Client or the Registration Server. Currently, re-logging is the only way to update this information.
- The user’s password has changed.
- Confirming the user’s identity for security reasons (usually done periodically)
Forcing the user to re-login can be done in the Admin Console. The user will be required to login again on all devices where the TeamDrive client is installed.
Identifying Externally Authenticated Users¶
When an “externally authenticated” user logs in to TeamDrive, the system needs to determine which External Authentication Service to use.
If the user is already registered on a TeamDrive Registration Server then
the server will have stored a reference to the associated External
Authentication Service in the user account. This is either determined
by a previous login, or by the External Authentication Service associated
with the Provider of the user (see USE_AUTH_SERVICE below).
If not already registered the External Authentication Service is identified using the domain (for example: “teamdrive.com”) of the user’s email address. In other words, the part of the email address following the ‘@’ sign.
Companies can register domains that they own with TeamDrive in order to ensure that all users with associated email addresses use a particular External Authentication Service. Domains are registered using the Admin Console as described in: Domains and Services.
As part of the registration, the domain must be associated with a External Authentication Service that has already been setup and deployed (as described above).
Note that if the domain of a user’s email address cannot be registered
with TeamDrive (for example, generic email addresses like those belonging to
gmail.com) then the only alternative is to “pre-register” the users, using
the Admin Console. In this case the Provider of the user must be
associated with a particular External Authentication Service as
specified by the AUTH_SERVICE_NAME Provider setting (see
AUTH_SERVICE_NAME for more details). In addition, USE_AUTH_SERVICE
must be set to True for the Provider.
If only certain users of the Provider should use external authentication
then you can set USE_AUTH_SERVICE to False and enable external
authentication for each user individually.
After Identifying the External Authentication Service to be used by a user the TeamDrive Client or Web Portal redirects the user to the login Web page of the authentication service.
Note, in earlier versions of the Registration Server it was necessary to manually
configure client settings (see CLIENT_SETTINGS) in order to use external
authentication. This is no longer required, and explicit client settings of
enable-login and enable-web-login can be removed.
Upgrading External Authentication Services¶
Note
Before upgrade make a backup copy of the “authservice” directory in your Apache docs folder. You may need to compare the new installation with the old in order to ensure backwards compatibility.
If you are running external authentication services setup prior to version 4.5.1 (12 April 2020) of the Registration Server, then “unnamed” services must be upgraded to a named authentication service.
In order to upgrade you must use the latest version of the various external authentication implementations. This code has been refactored to make upgrade easier in the future. In particular, code and customised pages have been separated so that future upgrades can be performed easily.
Begin by installing the PHP code of the authentication service, rename the
configuration file: *_config.php.example to *_config.php. All changes
you make to the configuration must be made to this file.
The upgrade procedure is as follows:
Configuration: Copy over configuration parameters to the new configuration file. Besides the configuration parameters that are specific to the service, you must ensure that the values
$user_secret_saltand$token_encryption_keyare correctly copied over to the new configuration file.User Secret Generation: Depending on the previous version of the External Authentication Service in use, the
$prev_user_secret_verparameter may need to be set eitherv1orv2(see Upgrading the User Secret Generation Method below).Service Name: Set the
$service_nameto the new name of the service. This must correspond to the name of service created on the Registration Server.When you access the “Login URL” for the first time, then service will check that the
$reg_server_nameand$provider_codecorrespond to the actual values of the service.You may need to set
$tdns_proxyto make it possible for the External Authentication Service to contact the TeamDrive Name Server.Customise Templates: Customise the
*_login.phpand*_verify.phppages for you purposes. Be careful to maintain the<?php ... ?>and<?= ... ?>elements in the pages.
Finally you need to add the name of your service to the PREVIOUSLY_UNNAMED_SERVICES
Provider setting (see PREVIOUSLY_UNNAMED_SERVICES for details).
Once this is done, test the External Authentication Service in a browser
before trying with a TeamDrive client. Setting the parameter $enable_debug
to true can help with testing, but be sure to set this back to false
before deployment.
Before deployment the new authentication service must be tested. In particular, you must compare the values returned after successful login with those returned by the previous External Authentication Service.
Upgrading the User Secret Generation Method¶
The “User Secret” is value generated by the External Authentication Service that is used by the user to access the Registration Server Key Repository. If the value changes, the user may loose access the the Space Keys in the repostory. As a result, it is important to ensure that this does not happen during the upgrade process.
Current generation is Version 3 (v3), as of Registration Server version 4.5.1. This is the most secure version of User Secret generation which uses the SHA256 HMAC algorithm. Previous versions, referred to as: Version 1 Generation (v1) and Version 2 Generation (v2) used an MD5 hashing.
If the previous External Authentication Service used either v1 or v2
generation then you must set the $prev_user_secret_ver parameter to
ensure no disruption of the Key Repository service.
Version 1 Generation was used by prior to Registration Server version 3.6.7 (6 November 2017), and Version 2 Generation was used prior to Registration Server version 4.5.1 (12 April 2020).
If you are not sure which version was used by the previous External
Authentication Service version, check the authservice/auth/auth_functions.php
file of the previous service.
If the file contains function get_user_secret_v3($user_id)
then Version 3 was in use. In this case no changes due to upgrade are
required and the $prev_user_secret_ver parameter can be left as is.
If the file contains function get_alt_user_secret($user_id), then
Version 2 Generation was in use. Set $prev_user_secret_ver to v2.
If the file contains function get_user_secret($user_id) and none of
the functions mentioned above, the Version 1 Generation was in use.
In this case, set $prev_user_secret_ver to v2.
If you have recently (within the last few years) upgraded from
Version 1 Generation to Version 2 Generation the the “safe” option is not
to upgrade to Version 3 Generation. In this case set
$prev_user_secret_ver to v2,v1.
Here is a summary of the $prev_user_secret_ver values:
""(blank): User Secret v3 generation will be used, no upgrade performed.v2: User Secret v3 generation will be used, and clients that previously used v2 will be upgraded.v1: User Secret v3 generation will be used, and clients that previously v1 will be upgraded.v2,v1: User Secret v2 generation will be used, and clients that previously v1 will be upgraded.
Please call TeamDrive for support for advice when upgrade your service, if you are unsure which value to use.
After setting the $prev_user_secret_ver you need to verify that the new
implementation of the external authentication service returns the same User Secret
value as the previous version.
To do this, compare the result page after login of both versions. Significant
are the values of the hidden fields in the page named td_user_secret and
td_alt_user_secret. If there is no td_alt_user_secret value in any
of the pages, then the td_user_secret must match for all user’s tested.
If there is a td_alt_user_secret value in the page returned by the
new version, then this must match with the td_user_secret in the current
implementation. In this case td_user_secret in the new page is the new
User Secret generated by v3 generation.
If there is a match, then the TeamDrive client will be able to access
the user’s Key Repository on the Registration Server. If not, and
$prev_user_secret_ver has been set correctly, then check the
$user_secret_salt configuration parameter. The value must be identical
to the value used by the previous version.
Implementation Details¶
The following section contains details of TeamDrive External Authentication Service implementation. This information is only relevant to developers who wish to implement and debug there own authentication service for TeamDrive.
The diagram below illustrates steps that constitute the external authentication procedure. Each step is described in the sections that follow.
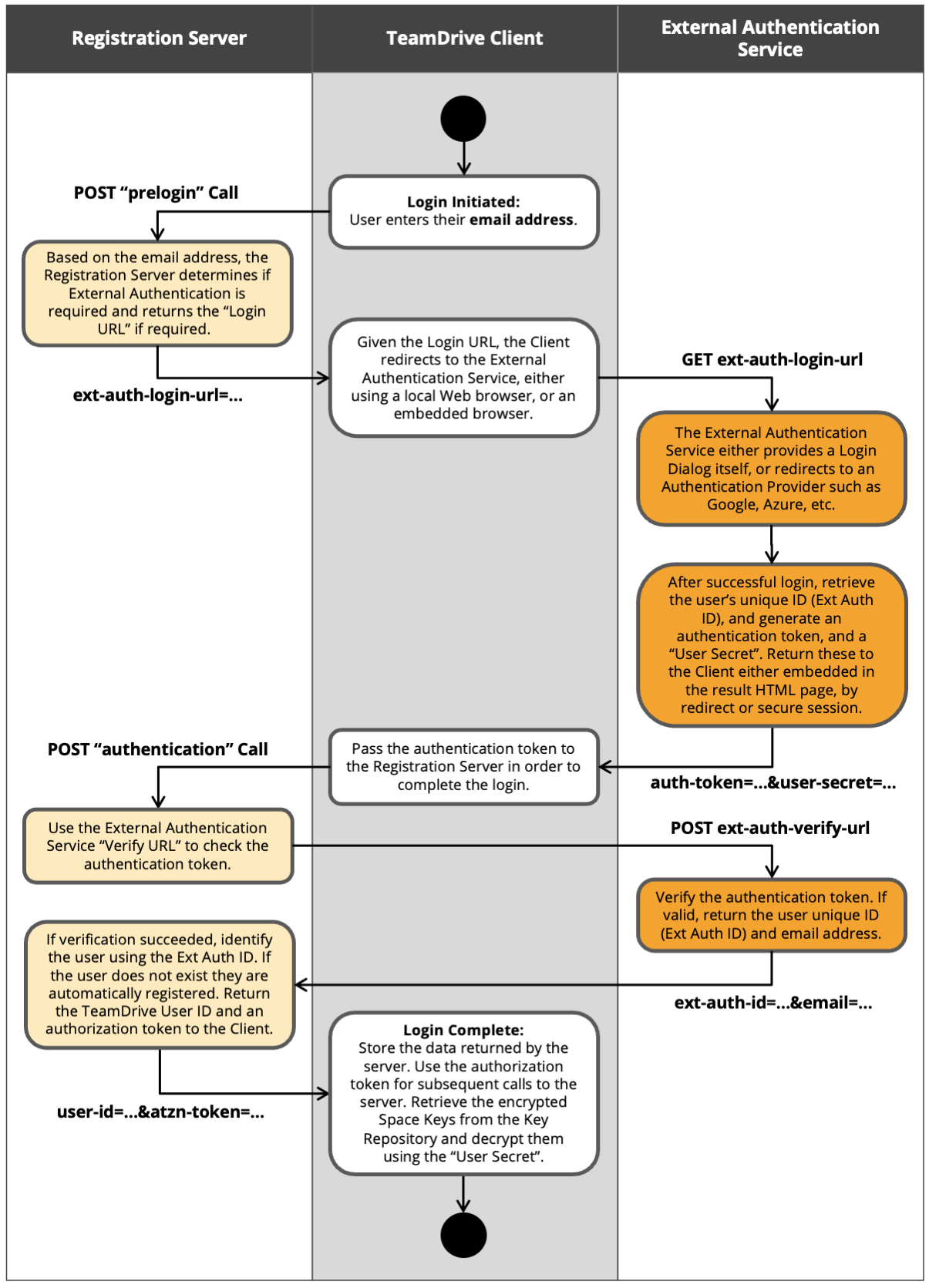
TeamDrive Client: Login Initiated¶
External authentication users must login using their email address. This is required because the domain of the email address is used to determine the External Authentication Service to be used, if the user is not already registered.
The client send the email address to the Registration Server in the “prelogin” call.
Registration Server: “prelogin” Call¶
The Registration Server determines the External Authentication Service, and returns the Login URL of the service to the client.
TeamDrive Client: Redirect to External Authentication Service¶
External authentication is a Web service, which must be accessed using a Web browser. Depending on the TeamDrive client in use, different methods are used to redirect the user to the browser based login.
These are as follows:
Embedded Browser¶
TeamDrive mobile Apps and older versions of the TeamDrive Desktop App use a
Web browser embedded in the Application to access the External Authentication
Service. The req=client Search Args is added to the Login URL to
indicate the Embedded Browser method.
On successful authentication the service returns the required data to the client App using hidden fields in the HTML result page.
HTTP Redirect¶
The TeamDrive Agent and the Web Portal have browser interfaces. So in this case,
all that is required to access the External Authentication Service is to redirect
the browser to the login page (using the Login URL) of the authentication
service. The req=portial&ref=<referrer-url> Search Args are added to the
URL to indicate that the HTTP Redirect method is to be used, and to specify
a “referrer URL”.
If login is successful the External Authentication Service redirects back to the origin using the referrer URL provided by the client, passing data back to the client as Search Args on the URL.
Session Based Access¶
The latest version of the TeamDrive Desktop App use “session based” browser access to perform external authentication. Authentication is initiated by launching a browser on the local machine and loading the Login URL.
Data is exchanged after successful login using a secure session that was established between the TeamDrive App and the External Authentication Service.
To create the session the client, first (before launching the browser) calls the
Login URL with the Search Arg: req=session, and receives a JSON reply
containing the Session ID (<session-id>) and an “Encrypted Session ID”
(<enc-session-id>).
The Search Arg sid=<enc-session-id> is then added to the Login URL used
when launching the browser. The TeamDrive App then polls the External Authentication
Service using the Search Args: req=status&sid=<session-id>, which returns
a JSON reply containing the status of the login process.
If login is successful then the req=status request the relavant login data to
the client in a JSON reply.
External Authentication Service: Login¶
When directed by the TeamDrive Client, the External Authentication Service either displays the login dialog itself, or redirects to an “Authentication Provider” such as Google or Azure.
On successful login, the service returns required data to the client using one of the methods described above. The most data returned includes the following:
Authentication Token¶
The Authentication Token is an encrypted character sequence containing the data that must be returned when the Registration Server requests verification of the token. It is prefixed with the name of the External Authentication Service.
This data in the token includes the Global Unique Identifier of the user as determined by the authentication provider, and the email address of the user.
Only the External Authentication Service on which the token originates can decrypt the token. An Authentication Token has an expiry time of 2 minutes, and a CRC32 check ensure prevent corruption.
The Authentication Token is returned to the TeamDrive Client which passes the token on the the Registration Server for verification of the login:
- Embedded Browser: The Authentication Token is returned in a hidden HTML
field called
td_authentication_tokenin the result page. - HTTP Redirect: The Authentication Token is returned as a Search Arg named
authTokenon the referrer URL. - Session Based Access: The Authentication Token is returned in an item
named
authTokenin the JSON reply.
User Secret¶
The User Secret is a hash of the Global Unique Identifier of the user as
provided by the authentication provider. The hash is generated using a secret
salt value ($user_secret_salt) known only to the External Authentication
Service.
The User Secret is used by the client to decrypt and access the Registration Server Space Key Repository belonging to the user.
The latest version (Version 3) of the hashing function uses the SHA256 HMAC algorithm.
On successful login the User Secret is returned to the client as follows:
- Embedded Browser: In a hidden HTML field called
td_user_secretin the result page. - HTTP Redirect: As a Search Arg named
userSecreton the referrer URL. - Session Based Access: In an item named
userSecretin the JSON reply.
Alternative User Secret¶
The Alternative User Secret is optional and will only be set if the Configuration
parameter $prev_user_secret_ver is set to a non-blank value. In particular: v1
or v2.
When $prev_user_secret_ver is set, the Alternative User Secret contains the
User Secret generated using a previously used version (either Version 1 or Version 2)
of the User Secret hashing algorithm.
This provide a way to upgrade to Version 3 hashing without users loosing access to their Key Repository. The TeamDrive Client will first use the User Secret to decrypt the Key Repository and if that fails the Alternative User Secret will be used. After decryption the Space Keys are re-encrypted using the User Secret so that after a while it is no longer necessary to return the Alternative User Secret.
If required, after successful login, the Alternative User Secret is returned to the client as follows:
- Embedded Browser: In a hidden HTML field called
td_alt_user_secretin the result page. - HTTP Redirect: As a Search Arg named
altUserSecreton the referrer URL. - Session Based Access: In an item named
altUserSecretin the JSON reply.
Profile Data¶
In addition to the values specified above, of which the Authentication Token and User Secret are required, the External Authentication Service can also return various profile data belonging to the user.
These values are all optional and include:
- Display Name: The full name of the user.
- Email: An alternative email for the user.
- Telephone: The home telephone number of the user.
- Mobile: The mobil telephone number of the user.
- Notes: Generally notes regarding the user.
- Language: Specifies the Language used by the user.
Registration Server: “authenticate” Call¶
After receiving the Authentication Token from the External Authentication Service, the TeamDrive client sends the value to the Registration Server using the “authenticate” API call.
The “authentication” Call retrieves the Verify URL for the External Authentication Service, and calls this URL, passing the Authentication Token.
The External Authentication Service decrypts the token, and checks that the token is valid and that it has not expired.
If all is correct then the External Authentication Service returns the data encrypted in the token to the Registration Server. This include the Global Unique Identifier of the user, also known as the “Ext Auth ID”, and the user’s email address.
The Ext Auth ID is used to find the associated TeamDrive user. If the user is found the Registration Server will update the users email address if necessary.
If the user is not found, then the Registration Server searches for a user with the given email address. If a user is found, then the server checks that the External Authentication Service associated with the user, matches the authentication service being used. If so, the server stores the Ext Auth ID in the user record.
The the user is not found, then the user is automatically registered by the server. If the email is already in use, an error will occur.
The Registration Server then generates an “Authorization Token” (known internally as the “Shadow Key”) for the user, and returns this, along with the TeamDrive User ID and other data relavent to the user such as Provider Code and Client Settings to the client.
TeamDrive Client: Login Complete¶
The TeamDrive Client stores the user data returned by the Registration Server. The Authorization Token is used for all subsequent calls to the Registration Server.
If Authorization Token is invalidated on the server, the client will re-initiate login.